
Imagine you want to invest in learning AI capabilities, helping you to serve your Scrum Team on a new level that the market is demanding these days. How would you start?!
This blog helps you start your AI journey powerfully.
Your first step has two main checklist categories:
Checklist 1: AI Fundamentals
Checklist 2: AI for Scrum Mastery

Let's check them one by one.
Checklist 1: AI Fundamentals
The first checklist has 5 items, including:
- Basics of AI
- AI Tools for Various Scrum Master Use Cases
- AI Fluency Framework
- Ethical & Responsible AI + Security
- AI Laws and Regulatory Approaches
Give each aspect a score out of 10 to evaluate your AI Fundamentals awareness.
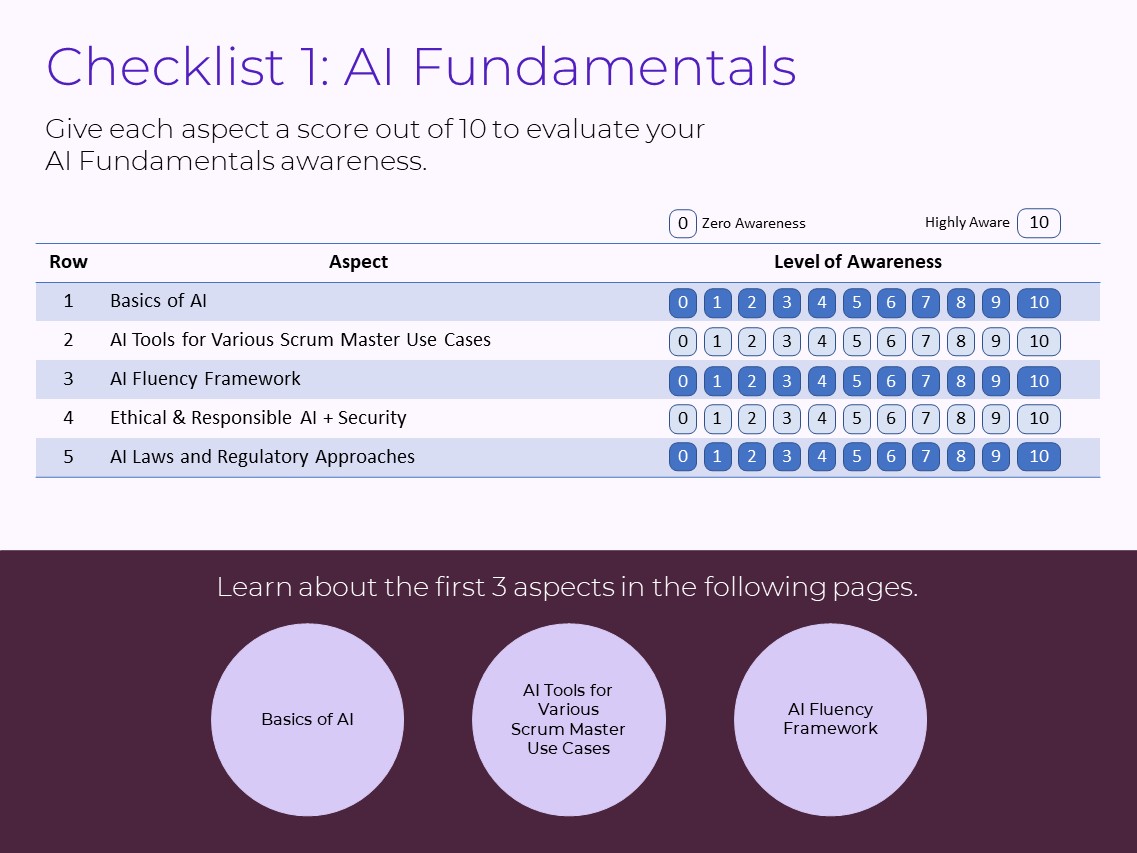
Let's talk about the first 3 aspects.
Basics of AI
Here are 20 key basic terms of AI that you should know:
1- AI (Artificial Intelligence)
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is a technology that enables computers to simulate human intelligence and problem-solving capabilities.
Examples are Siri or reading a car's plate number at the parking entrance.
2- Generative AI
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence models that can create new content, such as text, images, audio, or video.
Examples are ChatGPT or DeepSeek.
3- ANI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence)
Artificial Narrow Intelligence, or ANI, is a type of AI designed to perform a single specific task.
Examples are self-driving cars or defect detection in a factory line
4- AGI (Artificial General Intelligence)
Artificial General Intelligence, or AGI, is the potential form of AI that can perform any intellectual task a human can.
5- Agentic AI
Agentic AI refers to AI systems designed to autonomously make decisions, plan, and execute tasks to achieve goals with minimal human intervention.
6- AI Model
A model is an AI system that has been trained on a dataset to recognize patterns, make predictions, or generate new content.
Examples are GPT-4 model by OpenAI or Gemini 1.5 Flash model by Google.
7- Algorithm
An algorithm is a set of rules or instructions designed to enable machines to learn from data, make decisions, or perform tasks.
8- LLM (Large Language Model)
Large Language Model, or LLM, is a type of AI trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like language.
9- Multimodal
Multimodal describes models that can process and generate multiple types of data, like text, images, audio, and video.
An example is Gemini 1.5 by Google that can process and generate text, images, audio, video, and code.
10- ML (Machine Learning)
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data, identify patterns and make decisions or predictions.
11- DL (Deep Learning)
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to learn complex patterns and create highly accurate outputs.
12- Prompt
A prompt is a text input given to an AI model to guide its response or generate desired output.
An example is: Write an email to stakeholders, inform them of the scope and goal of the Sprint, and invite them to the upcoming Sprint Review.
13- Prompt Engineering
The process of designing effective prompts to generate better and desired responses.
14- Supervised Learning
Supervised Learning is a model training approach to learn from paired input-output labeled data to predict outputs for new, unseen inputs.
15- Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning is a model training approach where a model discovers patterns and structures within unlabeled data.
16- Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning is a model training approach where a model learns to optimize decisions based on receiving rewards and penalties for actions.
An example is when computers learn to play chess.
17- Diffusion Model
A diffusion model is a generative AI technique that learns by iteratively adding noise to data and then denoise it to create new outputs like images.
An example is that most AI images are generated by Diffusion Models.
18- RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation, or RAG, is an AI technique that enhances large language models by retrieving information from external sources to generate more accurate and context-aware responses.
An example is giving your company's HR policy document to a model, then your employees can ask how to use the company parking lots or how to have a work mobile phone.
19- Fine-tuning
Fine-tuning is the further training of a pre-trained AI model on a smaller, domain-specific dataset to enhance its performance for a particular domain.
Examples are fine-tuning a model for medical or legal domains.
20- Token
A token is the fundamental unit of text that an AI model processes, which can be a word, part of a word, or even a single character.
AI Tools for Various Scrum Master Use Cases
This is a complete suite of an AI toolbox for Scrum Masters:
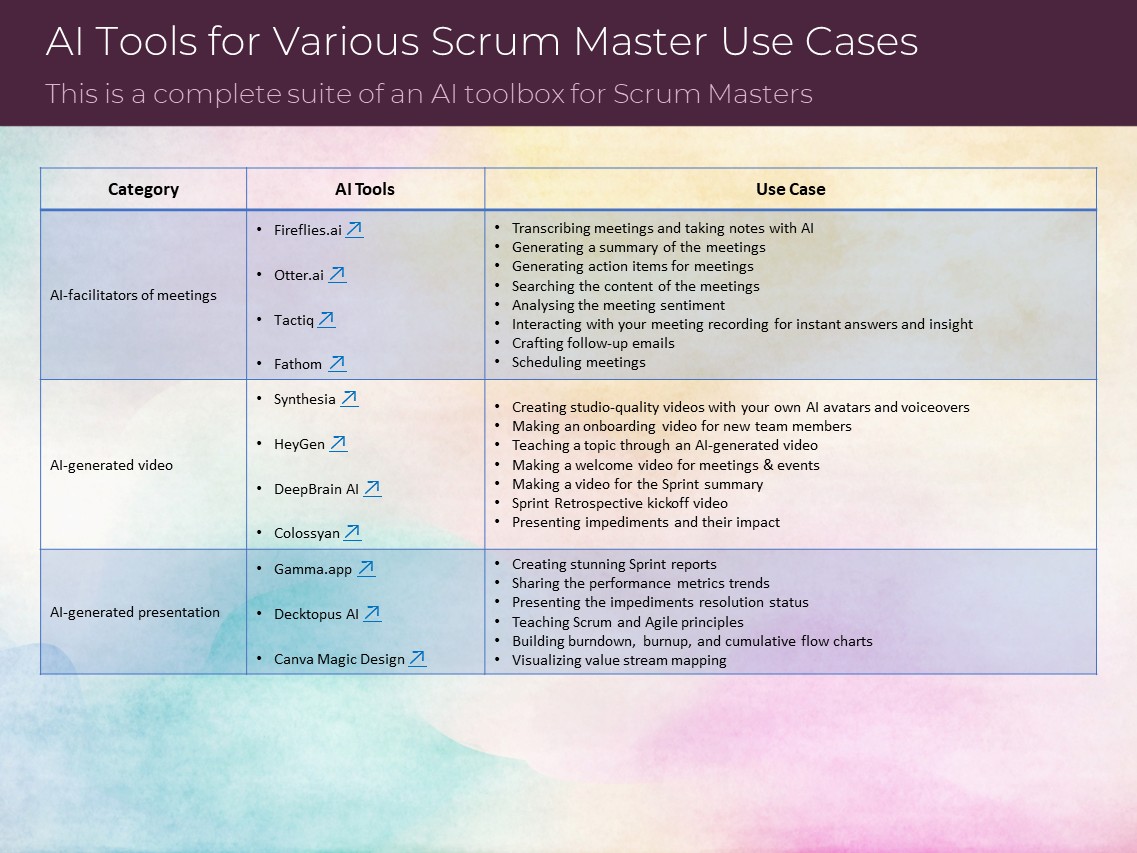
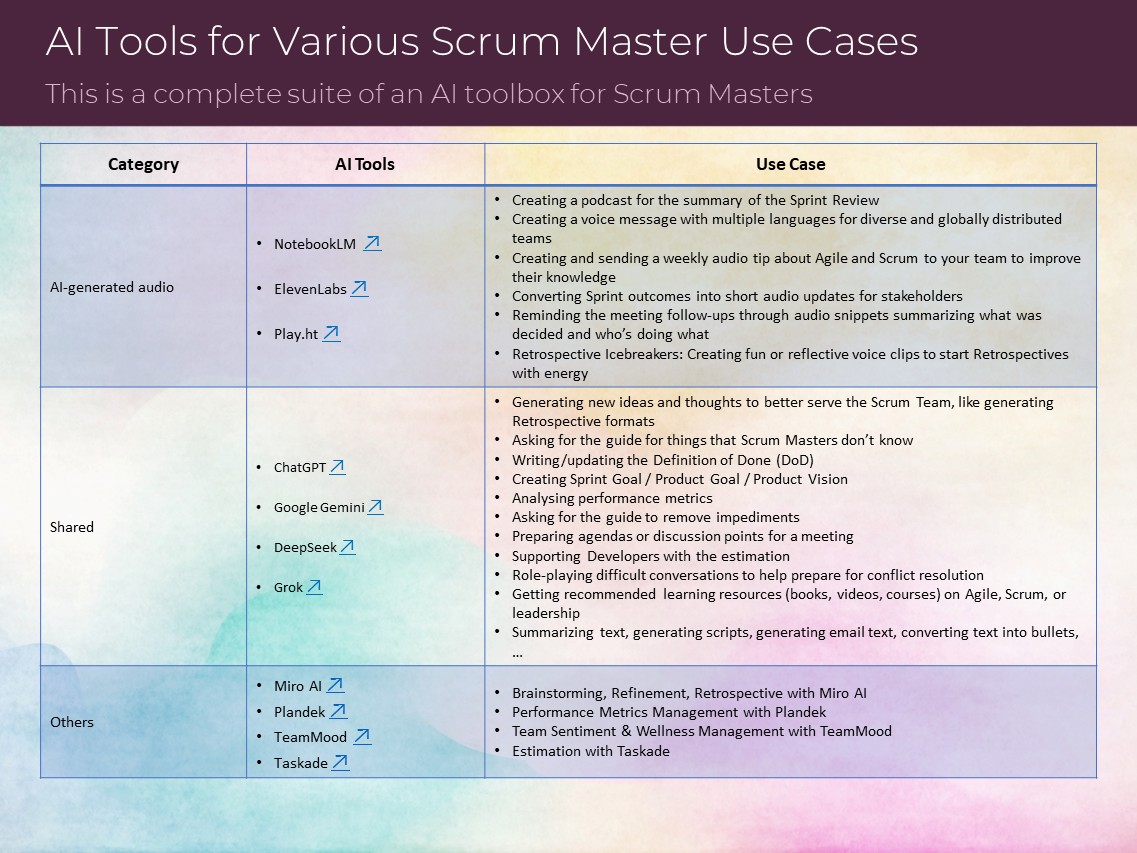
AI Fluency Framework
An AI-aware Scrum Master leverages AI within the boundary of the 4D AI fluency framework to ensure their interactions with AI are effective, efficient, ethical and safe.
This framework has four aspects:
1- Delegation
Setting goals and deciding whether, when and how to engage with Al.
2- Description
Effectively describing goals to prompt useful Al behaviors and outputs.
3- Discernment
Accurately assessing the usefulness of Al outputs and behaviours.
4- Diligence
Taking responsibility for what we do with AI and how we do it.

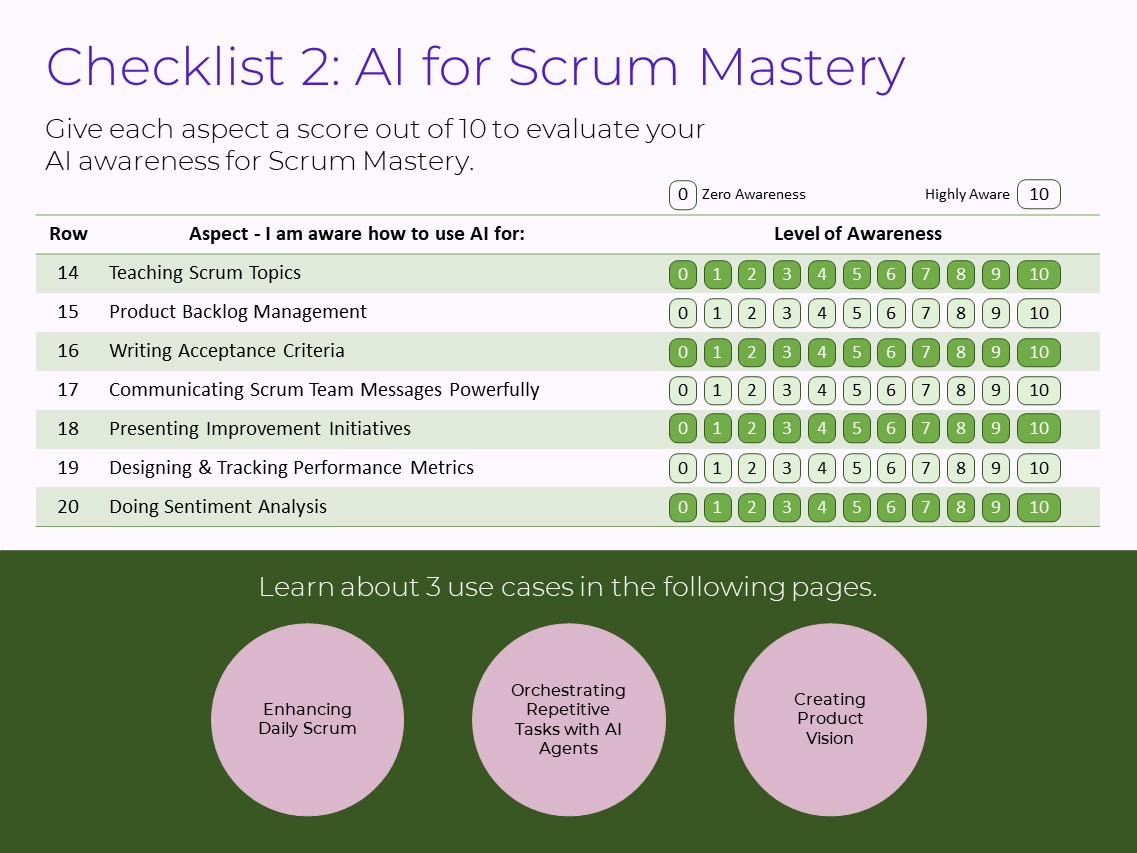
Checklist 2: AI for Scrum Mastery
The second checklist has 20 items, including:
- Facilitating Scrum Team Meetings & Collaboration
- Enhancing Sprint Planning
- Enhancing Daily Scrum
- Enhancing Sprint Review
- Enhancing Sprint Retrospective
- Enhancing Product Backlog Refinement
- Orchestrating Repetitive Tasks with AI Agents
- Creating Definition of Done
- Creating Product Vision (Product Goal)
- Creating Sprint Goal
- Resolving Conflicts
- Removing Impediments
- Coaching & Mentoring
- Teaching Scrum Topics
- Product Backlog Management
- Writing Acceptance Criteria
- Communicating Scrum Team Messages Powerfully
- Presenting Improvement Initiatives
- Designing & Tracking Performance Metrics
- Doing Sentiment Analysis
Give each aspect a score out of 10 to evaluate your AI awareness for Scrum Mastery.
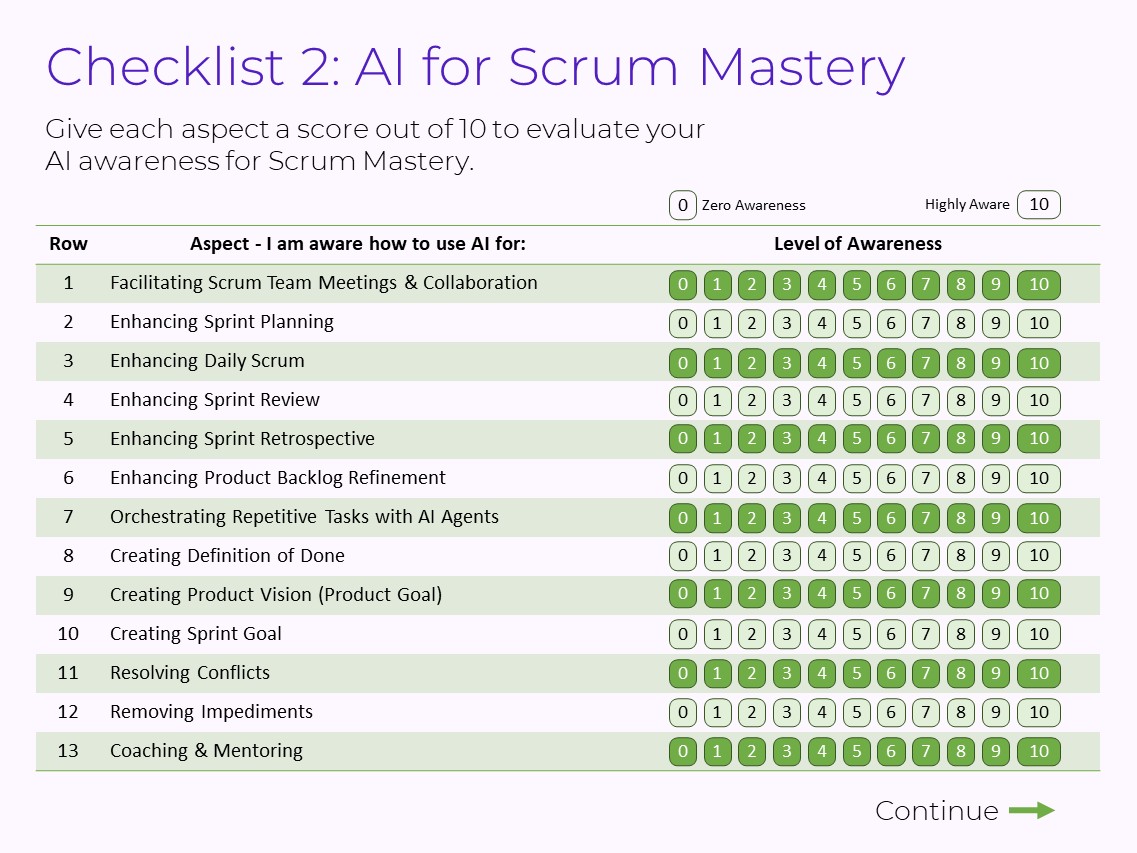
Let's talk about 3 use cases.
Enhancing Daily Scrum

1- Before Daily Scrum
Use AI to analyze your task management tools like Jira, Azure DevOps, etc. + your team communication tools like Slack, MS Teams, etc. to create your desired insights of the previous day, giving you input for today’s Daily Scrum, including:
- Stories stuck too long
- Work-in-progress violations
- Unplanned work (bugs, urgent requests, …)
- Any blocker
- Team sentiment
- The likelihood of achieving the Sprint Goal
- …
Result: The team walks into the Daily Scrum already aware of where inspection is needed, saving time and making it more effective.
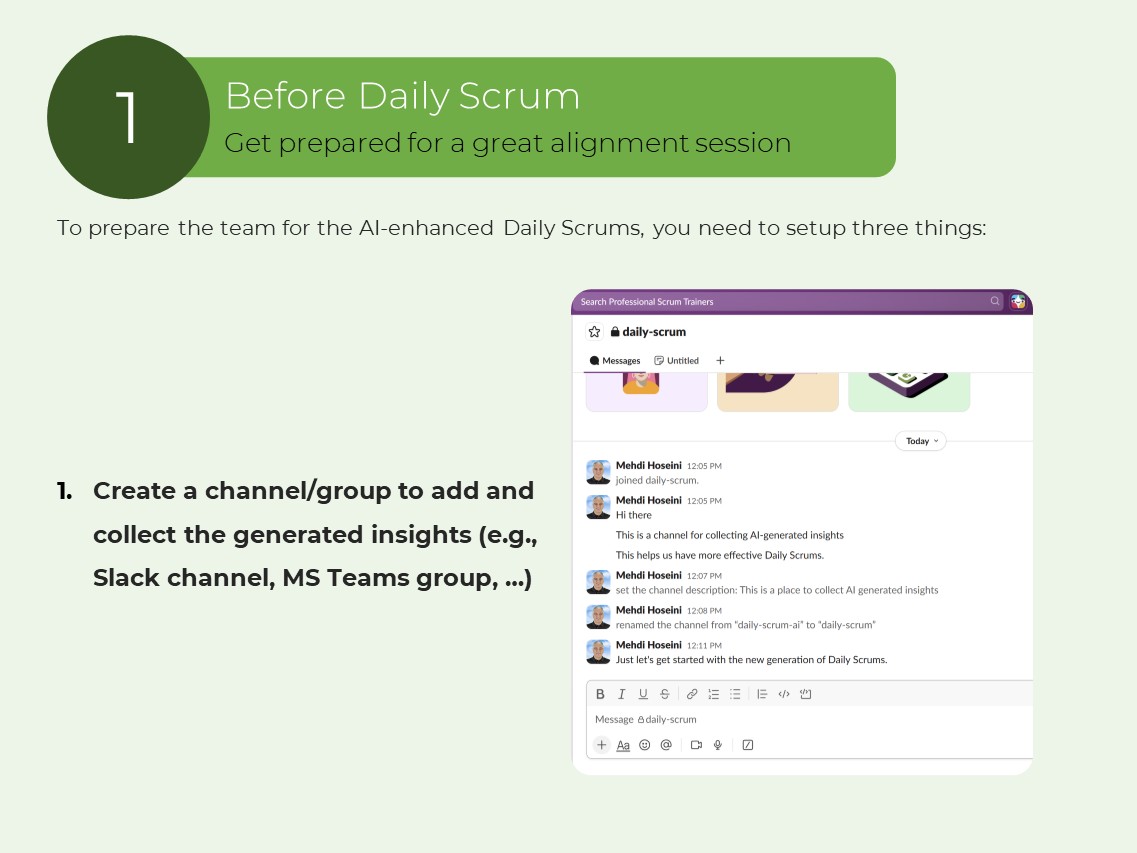
To prepare the team for the AI-enhanced Daily Scrums, you need to setup three things:
1.1. Create a channel/group to add and collect the generated insights (e.g., Slack channel, MS Teams group, …)
1.2. Create an AI Agent to communicate with your task management tools (Jira, Azure DevOps, …)
Schedule to run your AI Agent 10 minutes before the Daily Scrum each day to identify all changes over the past day, generate required insights, and add them to the Daily Scrum channel.
*** You can use Make.com, n8n, Zapier, etc. to create your AI Agents. My recommendation is Make.com, which is simple and user-friendly.

1.3. Create an AI Agent to connect with your communication tools (Slack, MS Teams, …)
Schedule to run your AI Agent 10 minutes before the Daily Scrum each day to go through all the conversations over the past day, generate required insights, and add them to the Daily Scrum channel.

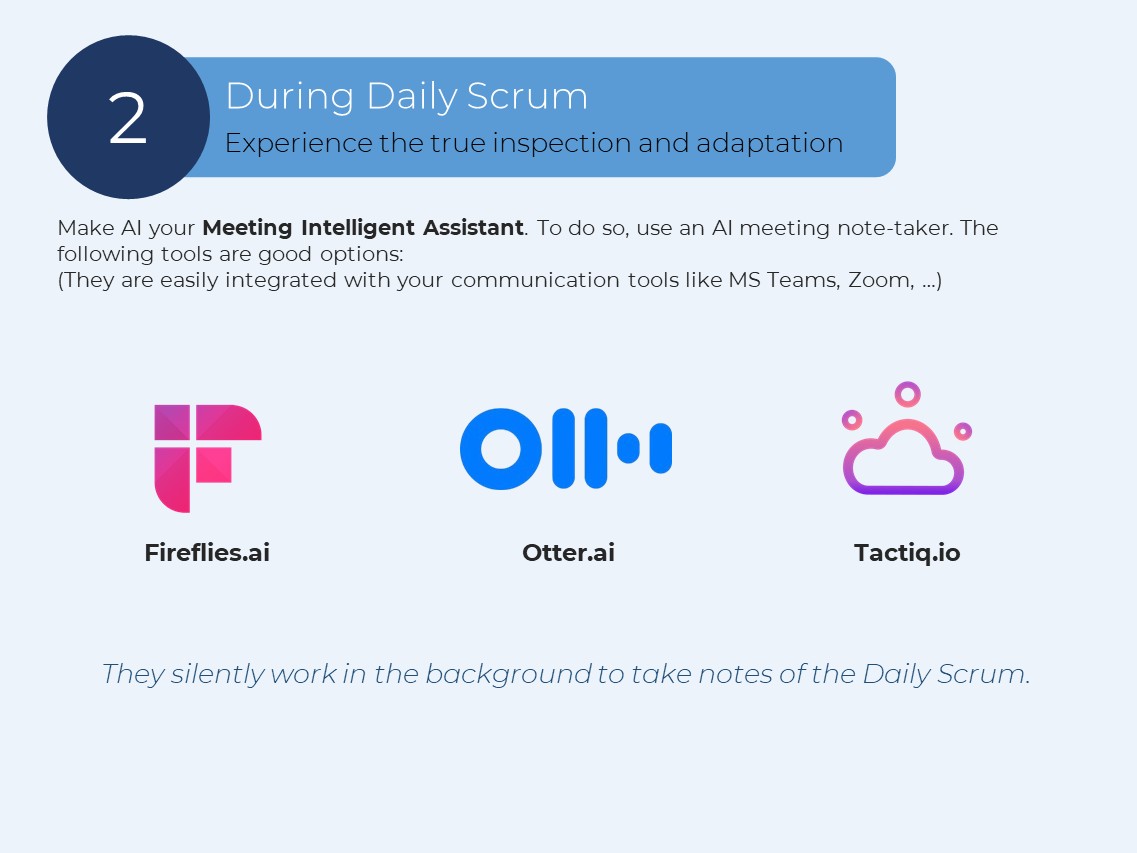
2- During Daily Scrum
Make AI your Meeting Intelligent Assistant. To do so, use an AI meeting note-taker. The following tools are good options: Fireflies.ai, Otter.ai, Tactiq.io
(They are easily integrated with your communication tools like MS Teams, Zoom, …)
They silently work in the background to take notes of the Daily Scrum.
Use two screens in your Daily Scrum as follows:
*** On the AI Help screen, you can access all AI inputs, including the Daily Scrum channel for AI-generated insights, in-meeting AI-generated alerts and flags, and more.

Daily Scrum happens in two parallel lines.
Line 1: Team
1- The team checks the insights of the past day generated just before the meeting by AI.
2- The team starts the conversation around inspecting the progress toward the Sprint Goal.
3- The team makes an actionable plan for today to maximize the likelihood of achieving the Sprint Goal.
4- The team shares the blockers and impediments and defines how it wants to deal with them.
Line 2: AI Assistant
Your AI assistant helps you by giving in-time alerts:
- Alert the team to return to the Sprint Goal
- Flag when the team drifts into problem-solving
- Flag repeated blockers
- Gently alert when someone exceeds their time
- Alert when the event timebox is over
Your conversations in the Daily Scrum should shift from activity reporting to Sprint Goal-oriented inspection.
3- After Daily Scrum
Setup your AI meeting note-taker and AI Agents to do the following things:
A- Create a summary of the Daily Scrum
B- List the blockers and how the team wants to deal with them
C- List the decisions for the day made in the Daily Scrum
D- Informing the Scrum Master about the impediments
E- Set separate meetings to solve announced problems and invite team members (for this item, you need to setup an AI Agent)

Sprint-level AI Insights
Scrum Masters can leverage the following Sprint-level AI-generated insights for the Sprint Retrospectives, private coaching conversations, and adjusting team agreements:
- Recurring blockers and impediments
- Stories that frequently spill over from one Sprint to the next Sprint
- Daily Scrums drifting into status meetings
- Daily Scrums drifting into problem-solving
- Stories repeatedly announced as “almost done”
- Same people always reporting blockers
- Who speaks most/least
- Whether updates are task-based vs. goal-based
- The positivity level of the Daily Scrums
- Adherence to the event timebox

Definition of a “Good” AI‑enhanced Daily Scrum
- Sprint Goal is the center of conversation
- Produces a clear, actionable plan for today
- Insights are generated and used
- Team members get in-time alerts
- Blockers are visible
- Is positive, productive, and ends early or on time
- Team leaves knowing exactly what to do next
Orchestrating Repetitive Tasks with AI Agents
AI Agent is an autonomous software system that uses artificial intelligence to perceive its environment, make decisions, and take action to achieve a specific goal without constant human intervention.
Imagine you receive dozens of customer support tickets each day. Your email provider is Outlook. Customers may sometimes request new features. Now, you want to set up an AI Agent to monitor incoming emails. If it discovers a new feature, add it to your Product Backlog, which is in Trello.
We call this AI Agent: User Story Collector. It can free up a lot of your time to use it for strategic work.
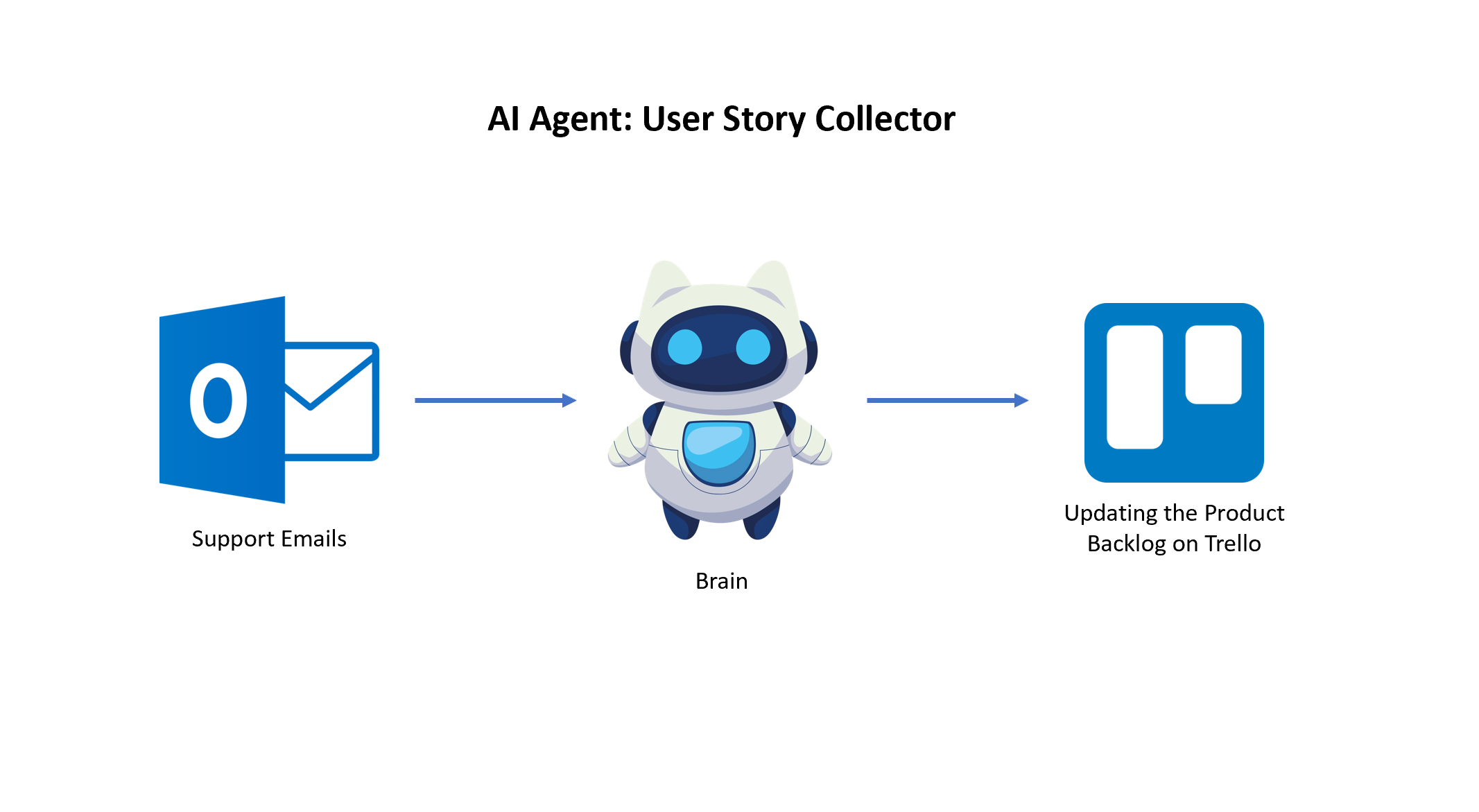
For building AI Agents, you can use Make.com, which is an amazing AI tool for automating your repetitive tasks.
I already recorded a video about building this AI Agent. Click here to watch it.

Creating Product Vision
Product Vision provides a shared, guiding "North Star" for the entire organization. It concentrates all teams’ energy into one single direction.
To create a compelling Product Vision, use the 3x3 framework, guiding you to think of the various aspects of your product.
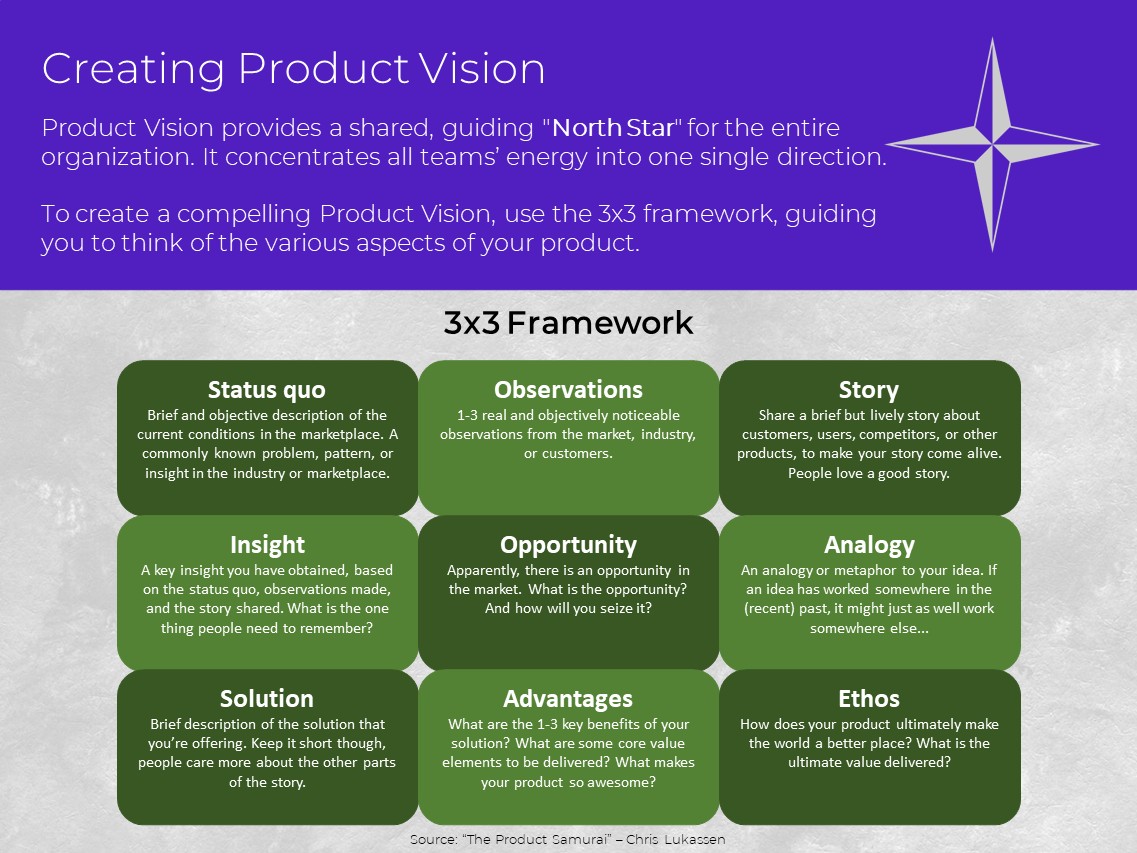
See how I created a compelling Product Vision video for a double-sided learning platform named “MetaLearn”. Click here to watch the video.
Process of creating a Product Vision video with AI
Step 1: Create the main concept of your Product Vision with the 3X3 framework.
Step 2: Ask an LLM tool (like Google Gemini) to create a scenario script for your vision video.
Step 3: Create a video for each scene of your vision (5-10 seconds) with an AI-generating video tool like Freepik.
Step 4: Give the narrator text to an AI-generating audio tool like ElevenLabs, choose a good voice, and download the result.
Step 5: Adding all these materials to a video editing tool like Camtasia to mix them and create the final result.

Now you have everything you need to start your AI journey. Good Luck!
-----------------------------------------------------
Are you a Scrum Master?
Then, if you want to invest in learning AI and become an AI-aware Scrum Master, attend my upcoming Professional Scrum Master – AI Essentials class. Click here to get more information about the class.
