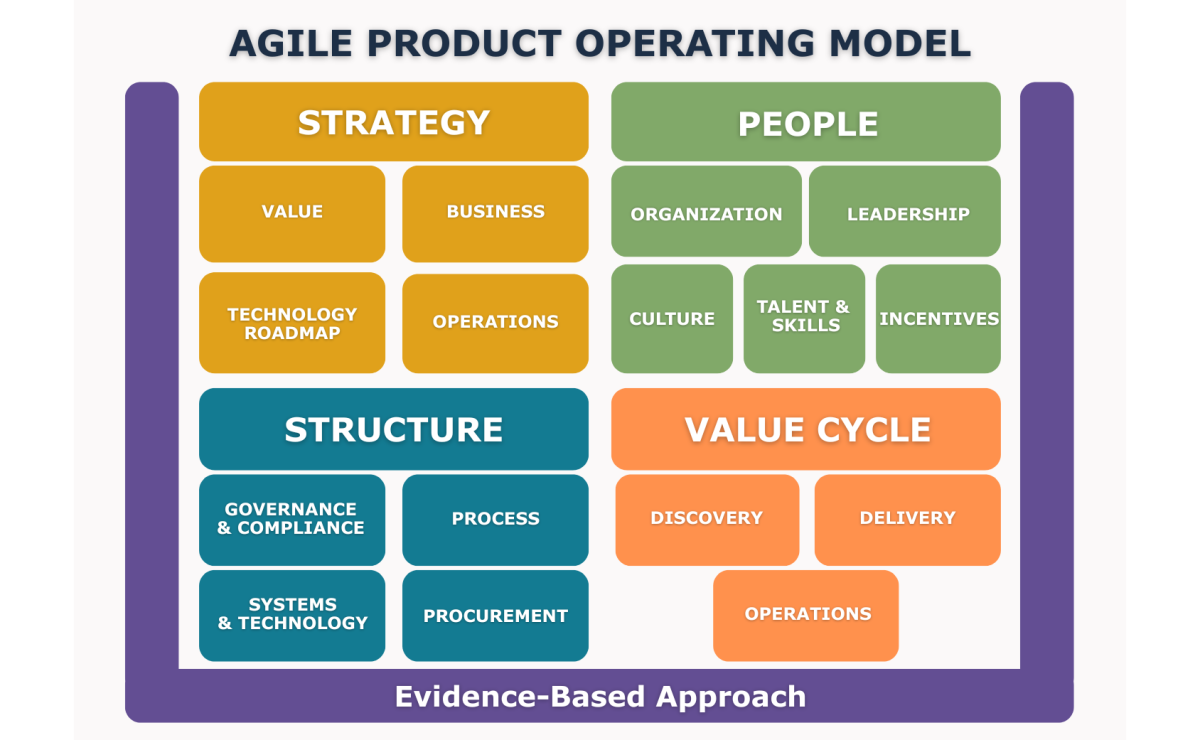
What is the Agile Product Operating Model (APOM)?
The Agile Product Operating Model (APOM), developed by Scrum.org, offers a comprehensive view of how organizations can deliver value effectively through a product-centric approach. It describes the capabilities that allow strategy, people, structure, and delivery to align — creating an adaptive system where value flows continuously and learning drives improvement.
Grounded in evidence-based management, APOM helps organizations connect vision and strategy to real outcomes in the market.
The Agile Product Operating Model presented in this article.
What are OKRs?
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) are a framework for setting goals and measuring outcomes that foster alignment, transparency, and focus.
Objectives define what we aim to achieve — ambitious, qualitative goals that inspire and focus the organization.
Key Results define how we measure success — quantifiable indicators that track progress toward the objective.
OKRs create a common language between strategy and execution, ensuring that teams work on what truly matters and that success is defined by outcomes, not activity.
How OKRs Support APOM
While APOM defines how an organization operates, OKRs define how it learns, aligns, and improves through measurable results.
Both frameworks share a foundation in empiricism: evidence, inspection, and adaptation.
- In Strategy, OKRs translate intent into measurable value.
- In People, they encourage purpose, engagement, and accountability.
- In Structure, they align governance and investment with desired results.
- In the Value Cycle, they reinforce learning and empiricism across discovery, delivery, and operations.
In short, OKRs are not an additional layer of process — they are the connective system that brings purpose, coherence, and visibility to how APOM operates.
Now, let's review in detal how OKRs can support the effectiveness of areas and features of APOM.
How OKRs Contribute to Each APOM Domain
APOM divides between 5 areas:
- Strategy
- People
- Structure
- Value Cycle
- Evidence-Based Approach
Let's see them go one by one:
🧭 STRATEGY
Defines why and where the organization competes, providing direction and measurable goals that link purpose to value creation.
🟨 Value
Defines what value means for customers, the business, and society. It helps teams focus on delivering outcomes that truly matter to users and stakeholders.
OKRs clarify and measure this definition of value, helping teams link daily work to improvements in customer experience, impact, or sustainability. They ensure that “value” is not abstract but observable through results.
🟨 Business
Establishes the goals and measures of business performance that sustain the organization. It connects market opportunities, competitiveness, and growth objectives.
OKRs align business ambitions — such as profitability, market expansion, or customer retention — with concrete product or operational outcomes. They allow business leaders to see progress empirically, not just through reports.
🟨 Technology Roadmap
Aligns long-term technology evolution with business and customer priorities. It ensures that technical decisions enable strategy rather than constrain it.
OKRs bring measurable focus to technology efforts, linking modernization, architecture, or platform investments to tangible business value such as speed, reliability, or scalability.
🟨 Operations
Translates strategy into execution by managing capabilities, dependencies, and resources effectively. It ensures operational coherence across teams and functions.
OKRs provide shared, cross-functional outcomes that integrate strategic direction with daily delivery. They help assess whether operations are not only efficient but also advancing strategic goals.
👥 PEOPLE
Centers on empowering and developing individuals and teams to deliver value effectively and sustainably.
🟩 Organization
Builds an environment where empowered, cross-functional teams can thrive and make meaningful decisions. It balances autonomy with clarity of purpose.
OKRs provide that shared clarity — giving teams freedom to innovate while maintaining alignment with organizational goals. They turn empowerment into accountability by defining outcomes teams commit to achieve together.
🟩 Leadership
Encourages leaders to inspire, coach, and remove obstacles rather than control or dictate. Leadership becomes a service to enable high performance.
OKRs shift leadership conversations from tasks and outputs to outcomes and evidence. They support leaders in fostering product thinking and empiricism, where success is measured by impact, not authority.
🟩 Culture
Shapes the shared values and behaviors that enable collaboration, learning, and adaptability. Culture determines how people respond to change.
OKRs help build a results-oriented culture grounded in transparency and reflection. Regular check-ins and reviews make progress and learning visible, creating a rhythm of collective improvement.
🟩 Talent & Skills
Develops the capabilities and competencies needed to create and evolve products successfully. It connects personal growth to organizational goals.
OKRs allow teams and individuals to align their learning objectives with measurable business outcomes. They ensure skill development is purposeful and directly contributes to product success.
🟩 Incentives
Reinforces behaviors that drive customer and business value, ensuring recognition aligns with contribution.
OKRs link incentives to meaningful results rather than effort or hours worked. They encourage intrinsic motivation and help shift evaluation from “what was done” to “what changed because of it.”
🧩 STRUCTURE
Defines how the organization is designed, governed, and supported to enable continuous delivery of value.
🟦 Governance & Compliance
Ensures accountability and transparency while preserving agility and innovation. It provides oversight based on trust and evidence, not control.
OKRs introduce an empirical governance model by defining measurable goals that demonstrate progress toward compliance and strategic intent. They turn governance into learning rather than reporting.
🟦 Process
Establishes how teams coordinate, prioritize, and improve work. Processes define how ideas move from concept to customer impact.
OKRs connect process improvement with real-world results, ensuring that optimizing flow or reducing waste directly contributes to measurable customer or business outcomes.
🟦 Systems & Technology
Provides the tools and infrastructure that enable delivery and collaboration across teams. It ensures stability, security, and efficiency.
OKRs measure how technical systems contribute to outcomes such as faster delivery, improved reliability, or lower costs. They help prioritize technical debt and investments based on their impact.
🟦 Procurement
Acquires products and partnerships that accelerate value delivery and innovation. It ensures vendors contribute to outcomes, not just deliverables.
OKRs align procurement strategy with measurable value creation, allowing organizations to evaluate suppliers based on shared results and long-term impact.
🔁 VALUE CYCLE
Represents the continuous flow of discovering, delivering, and improving value for customers and stakeholders.
🟧 Discovery
Identifies opportunities, validates assumptions, and ensures the team is solving the right problems. It turns uncertainty into learning.
OKRs provide focus for discovery work by defining what evidence will demonstrate success. They ensure learning goals are explicit, measurable, and directly tied to customer impact.
🟧 Delivery
Brings validated ideas to life through iterative delivery of working product increments. It turns knowledge into outcomes.
OKRs connect delivery efforts to measurable value, reinforcing Scrum’s empirical cycle. Teams can inspect their results against OKRs and adapt based on real-world evidence, not assumptions.
🟧 Operations
Ensures reliability, support, and continuity of delivered value. It focuses on sustaining trust and satisfaction after delivery.
OKRs extend beyond release to track whether the delivered product continues to generate value. They make service quality, uptime, and user satisfaction part of the outcome equation.
Evidence-Based Alignment
Both APOM and OKRs rely on empiricism — making decisions grounded in evidence and continuously adapting based on what is learned.
Together, they form a system for strategic agility:
- APOM defines how an organization operates to deliver value.
- OKRs define how it aligns, learns, and measures progress toward that value.
OKRs don’t replace APOM — they activate it.
They make strategy actionable, people aligned, structure purposeful, and value cycles measurable.
Thinking Forward
When considered separately, APOM and OKRs each offer powerful but distinct benefits.
APOM provides a holistic structure for how an organization delivers value — aligning strategy, people, and systems around continuous improvement.
OKRs, meanwhile, create focus and accountability for what success looks like, turning ambition into measurable progress.
But when combined, they form a complete system of strategic agility: APOM defines how value flows, and OKRs define how success is proven.
Together, they help organizations not only do the right things but also know, with evidence, that those things are truly making a difference.
🤔 Give me feedback!
Is this article relevant for you? How could I improve it?
Please share your feedback in the comments below!